Imagine software development as a busy railway network. Each train (feature) must run on time, avoid collisions, and eventually arrive at the same central station (the main codebase). Branching strategies are the tracks that keep this system running smoothly — ensuring collaboration, version control, and continuous delivery don’t descend into chaos.
From GitFlow’s structured rails to GitHub Flow’s streamlined routes and Trunk-Based Development’s express line, each strategy offers unique advantages. Choosing the right one depends on your project’s complexity, release cadence, and team culture.
The Foundation: Why Branching Strategies Matter
Branching strategies serve as blueprints for collaboration. They dictate how developers work independently, merge code safely, and manage releases. Without them, codebases quickly spiral into confusion, with conflicting versions and unstable builds.
A well-defined branching model improves visibility, enforces discipline, and supports continuous integration — the lifeblood of modern DevOps practices. For professionals keen to master such collaborative frameworks, enrolling in a DevOps training institute in Bangalore can help build the practical understanding needed to manage repositories effectively in real-world teams.
GitFlow: The Structured Railway
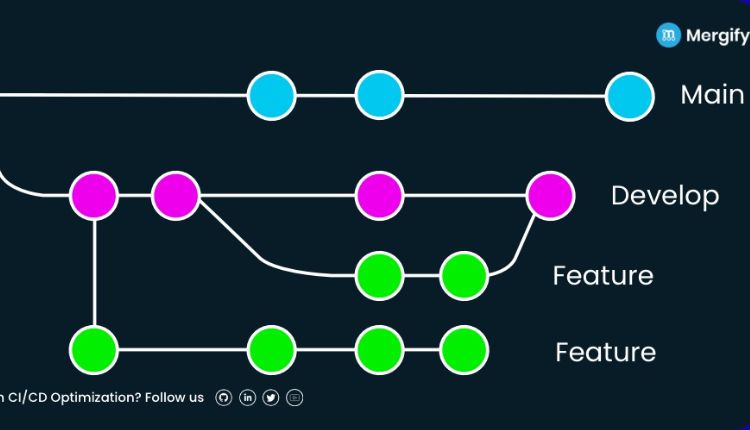
GitFlow is like a city metro with multiple well-marked routes — feature, release, and hotfix branches — all connecting through a controlled central line. It is highly structured, making it ideal for enterprise environments with fixed release schedules.
In GitFlow, every new feature has its own branch, releases are planned meticulously, and bug fixes follow clear lanes. While this ensures order and traceability, it can slow things down in fast-moving projects. Developers spend more time merging, reviewing, and managing pull requests — a trade-off between speed and stability.
Still, for long-running projects requiring strict quality control and documentation, GitFlow remains one of the most reliable systems.
GitHub Flow: The Agile Shortcut
If GitFlow is a metro, GitHub Flow is a sleek bike lane — minimal, agile, and designed for speed. It fits modern teams practising continuous delivery, where releases happen multiple times a day.
GitHub Flow simplifies the process: developers create a branch, build and test features, and merge them into the main branch via pull requests once reviewed. The result is faster iteration and a steady deployment rhythm.
However, GitHub Flow works best for projects with automated testing and strong CI/CD pipelines. Without these safeguards, quick releases can introduce regressions. It’s perfect for startups or web-based teams where adaptability matters more than rigid structure.
Trunk-Based Development: The Express Line
Trunk-Based Development (TBD) is the expressway of branching strategies. Instead of maintaining long-lived branches, developers work in short, frequent commits directly to the main branch (the “trunk”).
This approach prioritises collaboration and rapid feedback. Teams can integrate code continuously, detect issues early, and reduce merge conflicts. However, it requires trust, discipline, and strong automated testing — because changes move fast and mistakes propagate quickly.
For teams that embrace CI/CD and prefer smaller, incremental improvements over massive feature releases, TBD offers unparalleled agility. It reflects the essence of modern DevOps — moving at speed while maintaining quality.
Professionals learning through a DevOps training institute in Bangalore often practice Trunk-Based Development scenarios to experience the pace and precision required for real-world agile environments.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Team
Selecting a branching strategy isn’t about which is “best” — it’s about which fits your team’s workflow.
- For structured releases and enterprise projects: GitFlow provides clarity and control.
- For fast-moving startups or web teams: GitHub Flow ensures flexibility and continuous deployment.
- For mature agile teams with strong automation, Trunk-Based Development delivers unmatched speed and collaboration.
Factors like team size, release frequency, and risk tolerance play crucial roles in this choice. The key is alignment — ensuring the branching strategy supports rather than hinders development momentum.
Conclusion
Branching strategies form the invisible framework behind every successful DevOps workflow. Whether your team thrives on structure, speed, or simplicity, the right approach transforms collaboration into a seamless flow of innovation.
Like choosing between express and local routes, understanding when to use GitFlow, GitHub Flow, or Trunk-Based Development can mean the difference between smooth releases and constant derailments.
By mastering these strategies, developers and DevOps professionals ensure that every new feature arrives on time and in perfect sync — keeping the software “train” running safely toward continuous delivery.